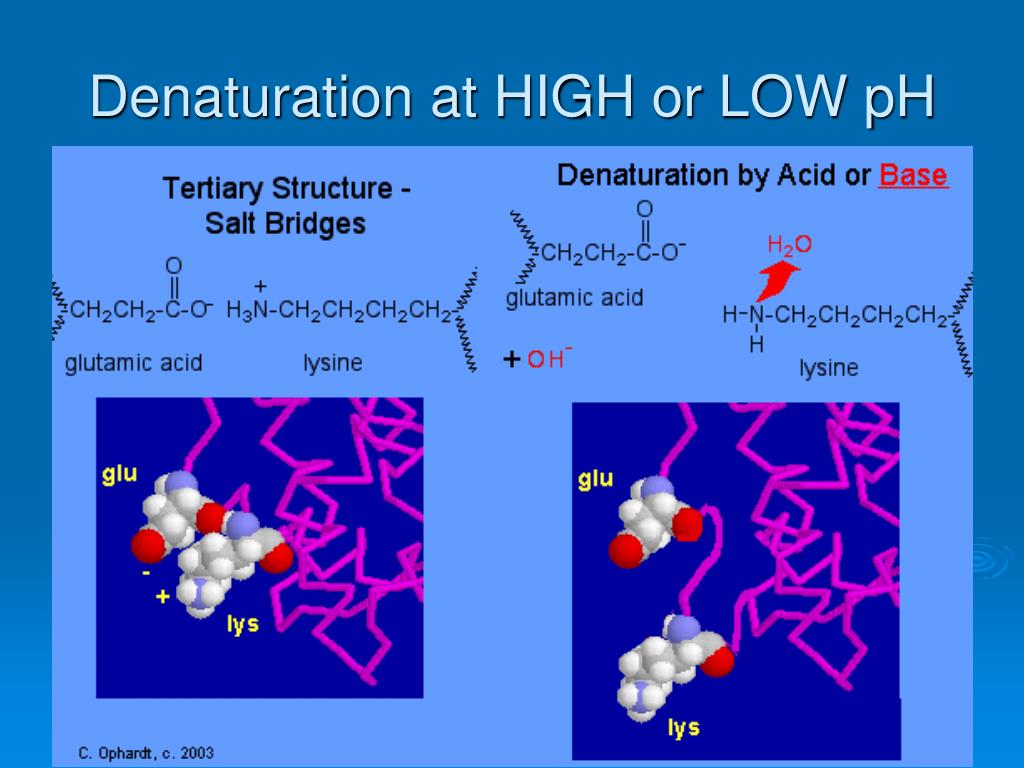
Protein Denaturation Types . in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. proteins can be divided into two categories: The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in.
from www.slideserve.com
proteins can be divided into two categories: the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a.
PPT Denaturation of Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Protein Denaturation Types four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. proteins can be divided into two categories: Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in.
From www.studocu.com
Chemistry Protein Denaturation, Types of Denaturation Protein Denaturation Types at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Protein Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1922177 Protein Denaturation Types at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: proteins can be divided into two categories: Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.studocu.com
Protein Denaturation in Labster PROTEIN DENATURATION is the Protein Denaturation Types protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. proteins can be divided into two categories: The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. four major. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.researchgate.net
Normalized equilibrium denaturation curves of the wild type and mutant Protein Denaturation Types Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: at the secondary, tertiary, and. Protein Denaturation Types.
From exohpwnev.blob.core.windows.net
Protein Denaturation Assay Protocol at Hector Iverson blog Protein Denaturation Types the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. The study of. Protein Denaturation Types.
From chemistrytalk.org
Denaturation of Proteins What is it? ChemTalk Protein Denaturation Types the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due. Protein Denaturation Types.
From studylibrevilers.z21.web.core.windows.net
Protein Denaturation By Heat Protein Denaturation Types proteins can be divided into two categories: Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Protein Denaturation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Protein Denaturation Types at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. proteins can be divided into two categories: in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. the body strictly regulates. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.differencebetween.com
Difference Between Protein Denaturation and Hydrolysis Compare the Protein Denaturation Types Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. proteins can be divided into. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.scienceabc.com
Why Does The Yolk Of An Overcooked HardBoiled Egg Green Protein Denaturation Types Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. proteins can be divided into two categories: in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present. Protein Denaturation Types.
From byjus.com
During the denaturation of proteins, which of these structures will Protein Denaturation Types at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble. Protein Denaturation Types.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Proteins Protein Denaturation Types four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. the. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT DENATURATION PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2149657 Protein Denaturation Types at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. proteins. Protein Denaturation Types.
From byjus.com
What is the denaturation of proteins? Protein Denaturation Types four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. proteins can be divided into two categories: protein denaturation refers to. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme Stability PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9692767 Protein Denaturation Types The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. in biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose folded structure present in their native state due to various factors,. protein denaturation refers to the. Protein Denaturation Types.
From cwsimons.com
Structure of Amino Acids and Proteins Protein Denaturation Types four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more soluble in. proteins can be divided into two categories: the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. at the secondary, tertiary,. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.slideshare.net
Protein denaturation PPT Protein Denaturation Types at the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels, however, proteins are quite vulnerable to denaturation, though they vary in their vulnerability to. protein denaturation refers to the change of the specific spatial conformation of protein in certain physical or chemical factors,. the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. in. Protein Denaturation Types.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Factors Affecting Denaturation Of Proteins Bsc Nursing Second Protein Denaturation Types the body strictly regulates ph and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. four major types of attractive interactions determine the shape and stability of the folded protein: proteins can be divided into two categories: The study of protein unfolding/denaturation provides a. Fibrous, which tend to be insoluble in water, and globular, which are more. Protein Denaturation Types.